- Overview
- Getting Started Guide
- UserGuide
-
References
-
ABEJA Platform CLI
- CONFIG COMMAND
- DATALAKE COMMAND
- DATASET COMMAND
- TRAINING COMMAND
-
MODEL COMMAND
- check-endpoint-image
- check-endpoint-json
- create-deployment
- create-endpoint
- create-model
- create-service
- create-trigger
- create-version
- delete-deployment
- delete-endpoint
- delete-model
- delete-service
- delete-version
- describe-deployments
- describe-endpoints
- describe-models
- describe-service-logs
- describe-services
- describe-versions
- download-versions
- run-local
- run-local-server
- start-service
- stop-service
- submit-run
- update-endpoint
- startapp command
- SECRET COMMAND
- SECRET VERSION COMMAND
-
ABEJA Platform CLI
- FAQ
- Appendix
Upload file to Datalake using Curl
Introduction
This documentation explains how to upload a file to Datalake using curl command.
Confirmation of Authentication Information
Since authentication is done with BASIC authentication, confirmation of authentication information is necessary.
You can choose either user authentication (USER_ID andPERSONAL_ACCESS_TOKEN) or datasource authentication (DATASOURCE_ID andDATASOURCE_SECRETS) as user id and password for basic authentication.
User Authentication
For details about authentication information, refer to How to check authentication information.
- User Name
user-{USER_ID} - Password
{PERSONAL_ACCESS_TOKEN}
$ curl --user user-1234567890123:8516bee2d1f3ae3299aaf9eac11e366ce5e83799 ...
Datasource Authentication
You will get the datasource information from channel details page .
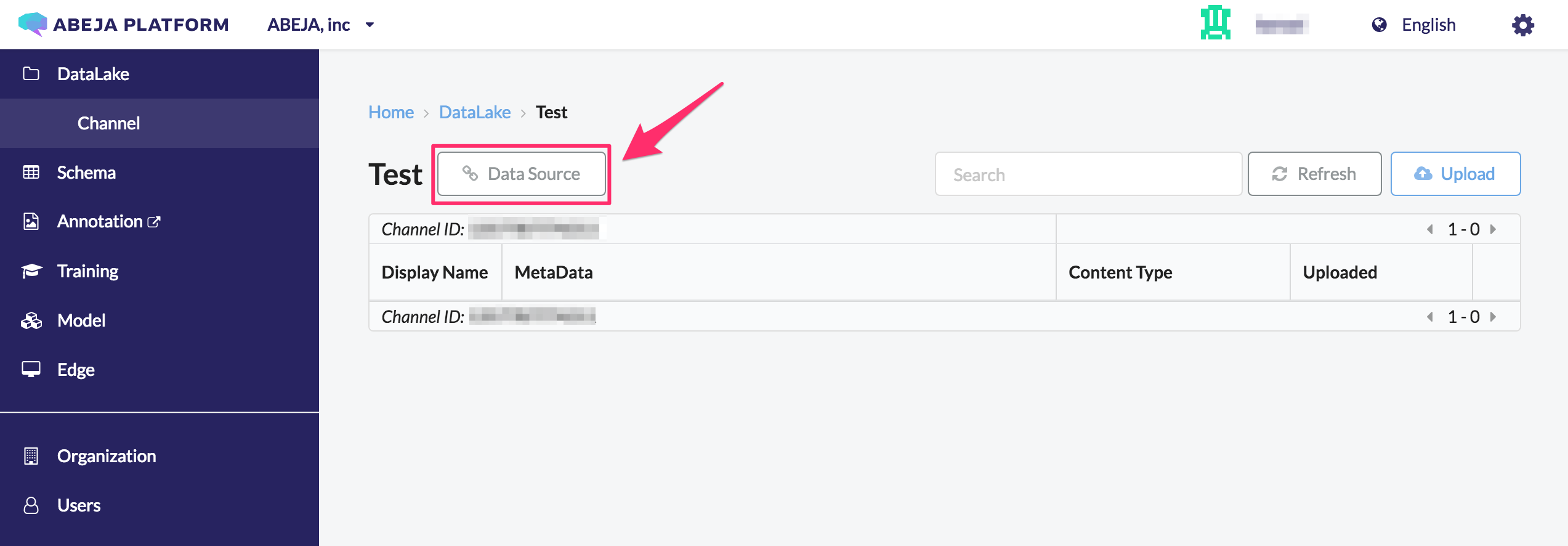
Get DATASOURCE_ID and DATASOURCE_SECRETS from the datasource list page of the channel.
- User Name
datasource-{DATASOURCE_ID} - Password
{DATASOURCE_SECRETS}
$ curl --user datasource-1234567890123:8516bee2d1f3ae3299aaf9eac11e366ce5e83799 ...
Datasource can restrict the channels that can transmit data. Also, since the datasource is not tied to a specific user, it is recommended to authenticate with a datasource to upload data from servers and sensors.
Upload file
You can upload any file to POST the contents of the file to https://api.abeja.io/channels/{CHANNEL_ID}/upload.
POST https://api.abeja.io/channels/{CHANNEL_ID}/upload
The following request to upload the file.
$ curl -X POST --header "Content-Type: image/jpeg" \
--header x-abeja-meta-filename:test.csv \
--user datasource-1234567890123:8516bee2d1f3ae3299aaf9eac11e366ce5e83799 \
--data-binary @/path/to/cat.jpeg \
https://api.abeja.io/channels/1234567890123/upload
Response (HTTP Body):
{
"file_id": "20170704T062222-cb6750bf-e679-48a6-ab96-0f4292e09f76",
"url_expires_on": "2017-05-17T13:24:57+00:00",
"uploaded_at": null,
"content_type": "image/jpeg",
"metadata": {
"x-abeja-meta-filename": "cat.jpeg",
"x-abeja-meta-label": "cat"
}
}
Metadata
Metadata can be added by specified in the form of x-abeja-meta-{FIELDNAME}:{FIELDVALUE} in the request header of temporary signed URL.
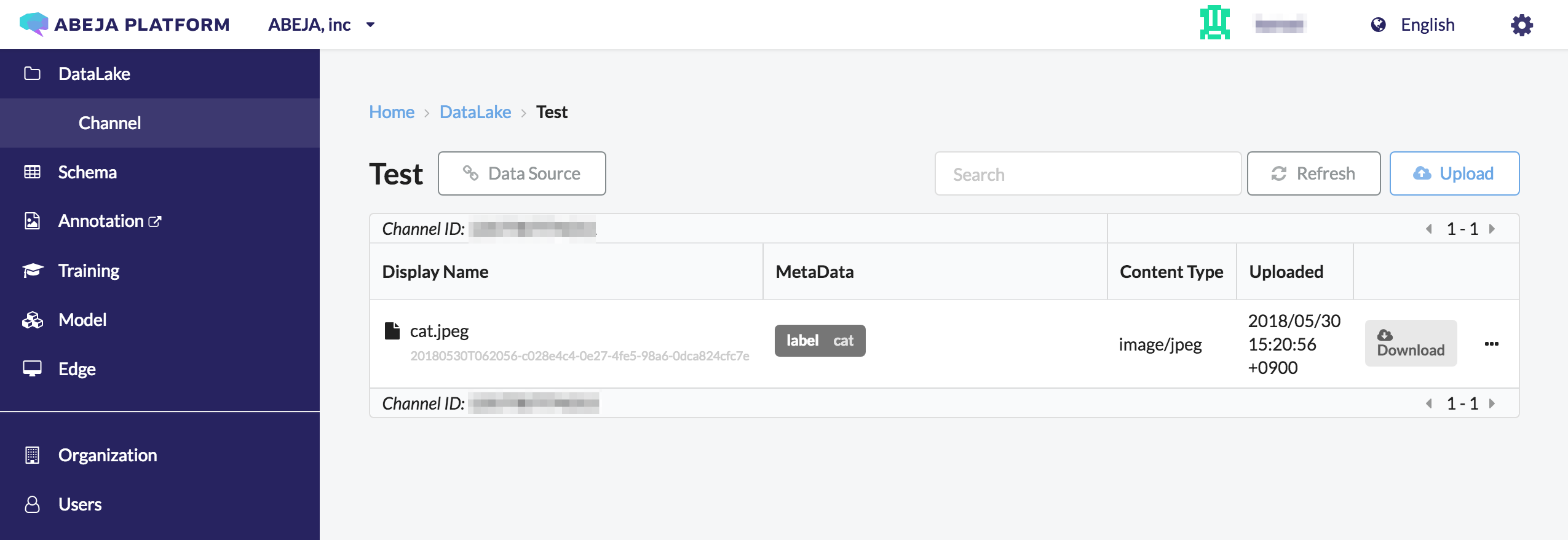
For the above case, cat.jpeg will store for filename key and cat will store for label key in metadata.
It is recommended to specify the filename key because it is displayed as the file name on the file list page.
Content-Type
Requested Content-Type will bet Content-Type of that file in Datalake. In this case, image/jpeg is specified.
If you do not specify Content-Type, default Content-Type is `binary/octet-stream`.
Maximum file size is 5TB what can upload using this request.
Confirm uploaded files
You can check the uploaded file from the Datalake details page of the console.